5 Life Insurance Options You Should Consider
Mar 21, 2024 By Triston Martin
In the event of your demise, life insurance establishes a financial safety net for your beloved family. The process of selecting an appropriate type can appear daunting. This article delves into five prevalent forms of life insurance, underlining their distinct features as well as advantages and disadvantages. To align your financial goals and circumstances, you must understand these options. This understanding will equip you with the knowledge needed to make an informed decision.
1. Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance furnishes coverage for a predetermined period, commonly between 10 and 30 years. If, and only if, the insured individual dies during this policy term, it offers an essential benefit to his beneficiaries. Thus, providing financial security in times of potential loss or tragedy. This particular form of insurance is not only clear-cut, presenting limited complexities,m but also frequently emerges as the cost-effective choice among various options available. Once the expiration of the term occurs, coverage definitively ceases. Policyholders then face a choice. Either to renew at an elevated premium or search for alternative coverage. This situation significantly diminishes its suitability in terms of long-term financial planning.
Diving deeper into term life insurance, we must underscore the fixed nature of premiums throughout the designated time. This offers a predictable budgeting tool for covering insurance costs. Such an aspect renders term life coverage highly appealing to those in pursuit of affordable policies during particular stages in their lives. Those rearing children or discharging mortgage debts, for instance.
- Consideration: Term life insurance is ideal for covering temporary needs, such as outstanding debts or income replacement during the years when dependents rely on the insured's financial support.
- Caution: Policyholders should carefully consider the length of the term to ensure it aligns with their financial obligations and objectives. Renewing or purchasing a new policy at an older age may result in higher premiums due to increased risk.
2. Whole Life Insurance
Lifelong coverage is offered by whole life insurance, contingent on the payment of premiums. Over time, it gathers cash value, functioning as a shield and an investment tool simultaneously. Policyholders possess the ability to borrow against this accrued cash value or relinquish their policies for its equivalent in cash. Whole life insurance provides stability and often emerges as a pricier option than term life insurance. Moreover, the returns on its cash value component may not equal those of other investment options.

Whole life insurance, in addition to bestowing death benefits. It [resents a tax-deferred growth component which is the cash value. This attribute equips policyholders with a fund reservoir. It's available for emergency access or can serve as supplementary retirement income.
- Fact: Whole life insurance premiums are typically higher than those of term life insurance due to the lifelong coverage and cash value accumulation.
- Note: Policyholders should review the policy's terms and conditions carefully, as surrendering the policy or borrowing against its cash value may have tax implications and affect the death benefit.
3. Universal Life Insurance
Universal life insurance offers flexibility in premium payments and death benefits. Policyholders can adjust the death benefit and premium payments to suit their changing needs. It also accumulates cash value, which earns interest over time. However, the flexibility comes with complexity, and policyholders need to monitor their policies closely to ensure they remain on track to meet their financial objectives. Universal life insurance may be suitable for individuals seeking customizable coverage and investment options.
Universal life insurance offers not just flexibility but also an advantageous feature: policyholders can allocate excess cash value to pay premiums. This allocation potentially decreases out-of-pocket expenses over time. Thus, this option benefits individuals experiencing fluctuating income or varying financial obligations.
- Consideration: Policyholders should review the policy's minimum interest rate guarantees and understand the impact of market fluctuations on the cash value component.
- Caution: Failing to maintain sufficient cash value or pay premiums on time may result in policy lapses or reduced death benefits, jeopardizing the coverage's effectiveness.
4. Variable Life Insurance
Combining death protection with investment options characterizes variable life insurance. Premiums allocation to diverse investment accounts, including stocks, bonds, or mutual funds is possible for policyholders. The performance of the selected investments dictates the fluctuation in both cash value and death benefit. Variable life insurance presents the potential for amplified returns; however, it also introduces escalated risk. Inferior investment performance may precipitate a decrease in cash value and death benefits. Thus, policyholders must critically evaluate their risk tolerance and investment expertise before selecting this form of insurance.
Variable life insurance, unlike traditional whole life insurance, enables policyholders to engage in market gains via investment-linked accounts. This distinct feature offers a potential for higher returns: thus it attracts individuals who are at ease with investment risk.
- Fact: Variable life insurance policies offer a range of investment options, allowing policyholders to diversify their portfolios based on their risk preferences and investment objectives.
- Note: Policyholders should regularly review their investment allocations and adjust them as needed to mitigate risk and maximize returns over time.
5. Indexed Universal Life Insurance
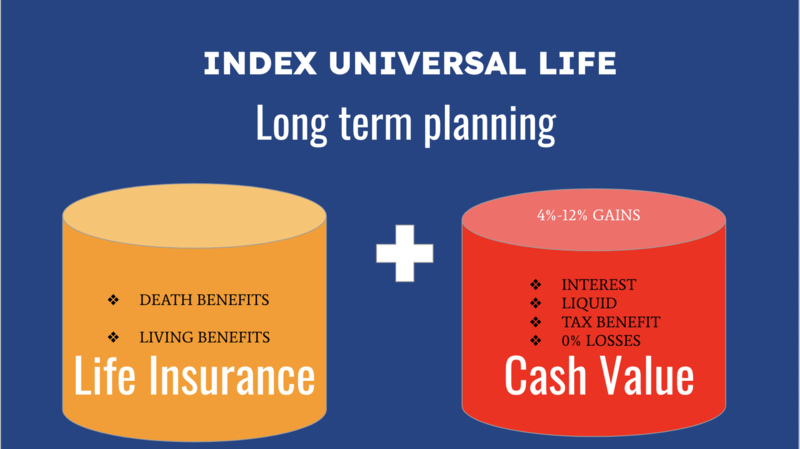
Indexed universal life insurance offers the flexibility of universal life insurance with the potential for higher returns linked to market indexes, such as the S&P 500. Policyholders can choose a fixed interest rate or link their cash value growth to the performance of the index. This type of insurance provides the opportunity to benefit from market gains while offering protection against market downturns through a guaranteed minimum interest rate. However, indexed universal life insurance may come with caps and participation rates that limit potential gains. Policyholders should carefully review the terms and conditions before making a decision.
Policyholders in indexed universal life insurance policies often customize their investments based on their risk tolerance and market outlook, thanks to a diverse range of indexing strategies. Through the careful selection of an appropriate strategy, they can potentially amplify the growth of cash value within their policies while reducing potential downside risks.
- Consideration: Policyholders should assess the policy's participation rate and cap limits to understand how much of the index's growth they can potentially capture.
- Caution: While indexed universal life insurance offers the potential for higher returns, it's essential to consider the impact of fees, expenses, and market volatility on the policy's performance over time.
Conclusion
Choosing the right life insurance requires careful consideration of your financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance. Each type of life insurance offers unique features and benefits, catering to different needs and preferences. By understanding the differences between term, whole, universal, variable, and indexed universal life insurance, you can select a policy that provides adequate protection and aligns with your long-term financial objectives. Consult with a licensed insurance agent or financial advisor to explore your options further and make an informed decision.

Can You Really Go to Jail for Debt

Debt Collection: Is There a Statute of Limitations?

FX in APAC: Key Insights and Implications for Regional Businesses

Funding Home Improvements: Qualifying for an FHA Loan

Top-Rated Funeral Coverage Providers

Explain in Detail: What Is a Financial Planner?

Making The Most Of Your HSA At Every Life Stage

Trading Options

How To Present A Gift Of Shares Of Stock

10 Ways to Improve Your Credit Score After a Foreclosure

Gross Debt Service Ratio
